
That is akin to having a safe and then making copies of the key and storing them in multiple locations that are accessible to the public.
#Lastpass security risks password
A recent survey by revealed 25% of password manager users reuse their master password on other sites. The problem is many users do not, despite the fact that a master password is a key to users’ entire digital lives. Then there is the volume of data that has been stolen – yet to be disclosed – so that will slow down any brute force efforts on individual accounts.Īll is well and good if users have set strong passwords.

If customers have set a password that is sufficiently complex, it would take weeks, months, or many many years to guess the right password. The hackers do not have master passwords in plaintext, so all is good in theory. LastPass uses 256-bit AES encryption, which is standard and secure. So, what does this mean? Well, the stolen vault data obtained by the hackers is fully encrypted, but if decrypted, that information includes website usernames and passwords, secure notes, form-filled data, and unencrypted website URLs.
#Lastpass security risks free
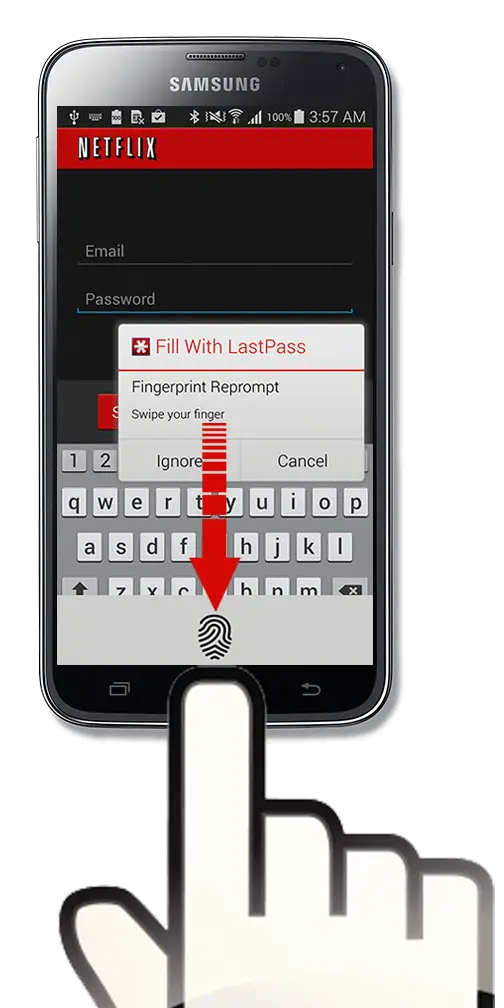
However, having a copy of encrypted password vaults means hackers have free reign to attempt brute force attempts on master passwords and the backup copy was stolen about 3 weeks ago, so the hackers have potentially had a considerable head start. Hackers cannot steal unencrypted password vaults, since the keys for decryption are stored locally by users. LastPass has discovered that in the second breach, the hacker(s) stole a copy of a backup of customers’ encrypted vaults from a storage container.Īs far as data breaches at password managers go, this is about as bad as it gets. The problem is for customers who have set weak master passwords because LastPass has announced that the hackers stole customers’ encrypted password vaults. This is important since users of password managers are putting all of their eggs in one basket by using a password manager, so zero knowledge is vital. LastPass does not know customers’ master passwords, so any hack will not allow those passwords to be obtained. LastPass, like many other password managers, operates under the zero-knowledge model. It is important to state that no customer master passwords have been breached.
#Lastpass security risks update
Now, LastPass has issued another update and said some customer password vaults are at risk. But no fear, customer password vaults were not affected. The data stolen in the first breach allowed a second hack. No customer data was involved in that breach, but then came the news that some customers were impacted, not in the first breach but a second, that was linked to the first.
It started with a breach of the LastPass developer environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
